Cats Hearing
Have you ever noticed your cat stalking something you cannot see or hear? Have you ever noticed your cat turning her attention to something or looking quickly in a certain direction while you sit dumbfounded wondering what she is doing? It's possible that she hears something you do not. Of course, that must mean that when you call your cat and she turns her head as if she doesn't hear you, she is choosing not to hear you. If you are familiar with "cat-titude," then knowing about your cat's hearing can come in handy.
Anatomy of the Cat's Ear
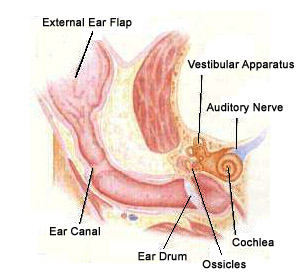
It all begins with the cat's outer ear, or pinna, which sits on top of the cat's head. The outer ear is controlled by about 30 different muscles that enable the cat to independently rotate each ear 180 degrees, and position one ear or both facing any sound the cat detects. The shape of the ear is designed to funnel sound down to the middle ear, where the tympanic membrane and three small bones, called auditory ossicles, transmit vibrations into the inner ear. The middle ear also contains a canal called the Eustachian tube that helps to equalize pressure in the ear. Within the inner ear is a curved bone, known as the cochlea. This is where the actual hearing mechanism is located, called the organ of Corti. It is here that small, sensitive hairs pick up sound vibrations and send them through the auditory nerve to the brain.
Each part of the ear, working together, gives the cat superb high-frequency hearing. Since mice squeak at an extremely high frequency, cats can hear these noises. This is no coincidence. Waiting in ambush and listening closely for the slightest squeak, cats' hearing allows them to be extremely effective hunters. To put it into better perspective, humans can hear frequencies from about 20 hertz to 20 kilohertz while cats, on the other hand, can hear frequencies from about 30 hertz to 60 kilohertz. Cats also have an incredible ability to localize sounds. They can hear and differentiate sounds three feet away whose sources are only three inches apart.
Because hearing is such a large part of a cat's life, it is important to try to shield them from loud, high-pitch noises such as sirens or loud whistles. It is also important to take sound into account when playing with cats. There are several toys on the market that mimic the sound of prey species to entice cats to play with them. This has the advantage of making the toy much more interesting. However, if the volume is irritating to you then it could be harmful to your cat. So, the next time your cat is sitting nearby and does not respond to your commands, remember that she can hear you loud and clear and is probably choosing to ignore you.
ref:http://theveterinarycentre.com